Endocrine Glands and Hormones
Endocrine Glands and Hormones: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Pituitary Gland, Insulin, Adrenaline, Melatonin, Thyroid Gland, Hormones, Adrenal Gland, Progesterone, Endocrine Glands, Pineal Gland, Estrogen, Thyroxine, Corticoids, Cortisol, Thymus and, Corpus Luteum
Important Questions on Endocrine Glands and Hormones
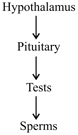
Study the following flow chart. Choose the correct sequence of hormones involved at each stage:
Damage to thymus in a child may lead to:
Pancreas produces
A person had to undergo a surgery in which a major portion of his pancreas was removed. Which of the following food constituents will he find especially difficult to digest?
Stress is reduced by:
Is hypothalamus an endocrine gland?
Select the number of hormones which are diabetogenic:
GH, Cortisol, Thyroxine, Insulin, Glucagon, Adrenaline, Aldosterone.
Hypothalamus directly controls the production of which of the following hormones?
Adrenal glands located in abdominal cavity are in close association with
Which one of the glands atrophies in adult?
Failure to produce Insulin leads to
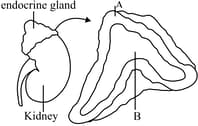
The figure below show the structure of endocrine gland of human body. The two labels, A and B are matched with their functions. Select the correct label and its appropriate function:
Which hormone enhances the movement of glucose from blood into the hepatocytes and adipocytes?
Which of the following is the main stimulus for the secretion of thyrocalcitonin?
The second half of the distal tubule and the cortical collecting tubule of kidneys are equipped with the Principal and Intercalated cells. Of these, the Principal cells reabsorb and excrete and are equipped with receptors for the hormone aldosterone. In primary hyperaldosteronism disease, there is an excess production of aldosterone which causes high blood pressure and imbalance. Spironolactone, a diuretic drug is generally used to treat these conditions. Choose the correct option for the mode of action of Spironolactone.
Which one out of the following hormone increases the blood glucose level by promoting glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis?
Which of the following hormone decreases blood glucose level?
The functioning of the kidneys is efficiently monitored and regulated by
Column I lists the endocrine structure and column JI lists the corresponding hormones. Match the two columns. Identify the correct option from those given
| Column I | Column II | ||
| A. | Hypothalamus | p. | Relaxin |
| B. | Anterior pituitary | q. | Estrogen |
| C. | Testis | r. | FSH and LH |
| D. | Ovary | s. | Androgens |
| t. | Gonadotropin releasing hormone | ||
The pancreas secretes
